Hisashi Ouchi is a name that will forever be etched in the annals of nuclear history. His tragic story serves as a stark reminder of the potential dangers associated with nuclear energy and the human cost of scientific accidents. In this article, we will delve deep into the life of Hisashi Ouchi, the incident that led to his exposure to lethal radiation, and the broader implications it has for nuclear safety and policy. We will also explore his legacy, and the ongoing conversation about the balance between energy needs and safety protocols.
Understanding the circumstances surrounding Hisashi Ouchi's life and the catastrophic event that occurred in 1999 is crucial in recognizing the importance of stringent safety measures in nuclear facilities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Ouchi's background, the incident that changed his life, and the aftermath that impacted many lives and policies regarding nuclear energy. By examining these elements, we can appreciate the lessons learned and the importance of maintaining safety in industries that pose potential hazards.
As we explore Hisashi Ouchi's story, we will also touch on the scientific and medical perspectives related to radiation exposure, the ethical considerations involved in nuclear energy production, and the societal implications of such incidents. This multifaceted approach will help readers gain a well-rounded understanding of the complexities surrounding nuclear energy and the human experiences intertwined with it.
Table of Contents
- Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
- The Incident at Tokaimura
- Understanding Radiation Exposure
- Medical Implications of Radiation
- Hisashi Ouchi's Legacy
- Nuclear Safety Regulations
- Ethical Considerations in Nuclear Energy
- Conclusion
Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
Hisashi Ouchi was born on March 29, 1965, in Japan. Growing up in a society that had a complex relationship with nuclear energy, Ouchi pursued a career in the nuclear field. His educational background included studies in nuclear engineering, which led him to work at the Tokaimura nuclear facility operated by the Japan Nuclear Fuel Conversion Company.
| Detail | Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Hisashi Ouchi |
| Date of Birth | March 29, 1965 |
| Occupation | Nuclear Engineer |
| Incident Date | September 30, 1999 |
The Incident at Tokaimura
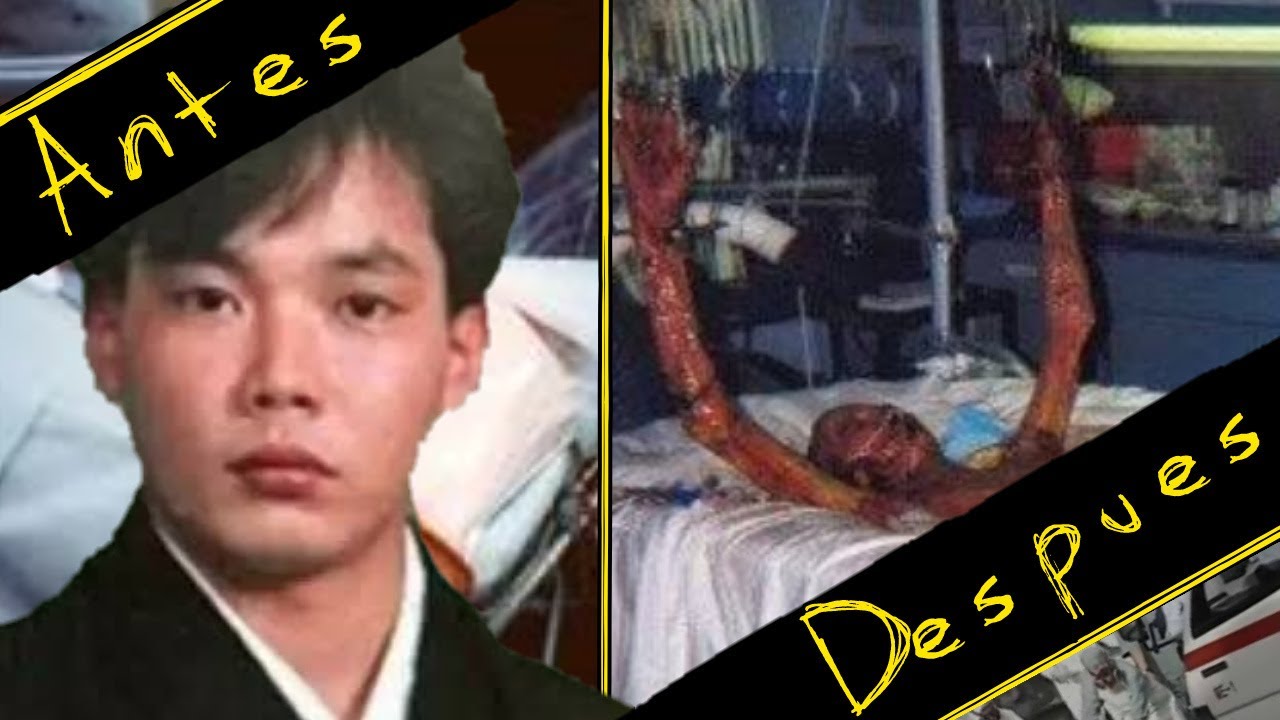
On September 30, 1999, a catastrophic accident occurred at the Tokaimura nuclear facility, where Hisashi Ouchi was working. A criticality accident took place due to a series of human errors and violations of safety protocols during the handling of uranium fuel. As a result, Ouchi and two of his colleagues were exposed to lethal doses of radiation.
Details of the Incident
- The workers were improperly mixing uranium fuel, leading to a criticality event.
- Ouchi received an estimated dose of 17 sieverts, far exceeding the lethal limit.
- The facility failed to implement safety measures, contributing to the severity of the accident.
Understanding Radiation Exposure
Radiation exposure refers to the absorption of ionizing radiation by the body, which can lead to severe health consequences depending on the dose and duration of exposure. In the case of Hisashi Ouchi, the exposure he experienced was catastrophic.
Types of Radiation
- Alpha particles: Heavy particles that can cause severe damage if ingested or inhaled.
- Beta particles: Lighter particles that can penetrate skin but are less damaging than alpha particles.
- Gamma rays: Highly penetrating radiation that can affect internal organs.
Medical Implications of Radiation
The medical implications of radiation exposure are severe and can lead to immediate and long-term health effects. In Ouchi's case, the medical team faced tremendous challenges in treating him due to the severity of his condition.
Short-term Effects
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe burns and skin damage
- Acute radiation syndrome (ARS)
Long-term Effects
- Increased risk of cancer
- Potential genetic damage
- Long-term organ damage
Hisashi Ouchi's Legacy
Hisashi Ouchi passed away on December 21, 1999, after suffering for nearly three months due to the effects of radiation exposure. His legacy is one of caution and a reminder of the human cost of scientific accidents. His case spurred discussions on the need for improved safety protocols in nuclear facilities worldwide.
Nuclear Safety Regulations
The Tokaimura incident highlighted significant gaps in nuclear safety regulations in Japan and worldwide. In response to the accident, various regulatory bodies implemented stricter safety measures and protocols to prevent such incidents from occurring in the future.
- Enhanced training for nuclear facility workers.
- Regular safety audits and inspections.
- Implementation of fail-safe mechanisms in nuclear operations.
Ethical Considerations in Nuclear Energy
The ethical considerations surrounding nuclear energy production are complex and often controversial. The case of Hisashi Ouchi raises questions about the balance between energy needs and the safety of workers and the public.
- Should the pursuit of nuclear energy come at the cost of human lives?
- What measures should be in place to protect workers in high-risk industries?
- How can transparency and accountability be ensured in nuclear operations?
Conclusion
In conclusion, the story of Hisashi Ouchi serves as a tragic reminder of the potential dangers associated with nuclear energy and the importance of adhering to safety protocols. His legacy continues to influence discussions on nuclear safety and ethics. It is vital for society to learn from such incidents to prevent future tragedies and ensure the well-being of workers and the community.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts on nuclear energy safety and the lessons learned from the Tokaimura incident. Your comments and insights are valuable as we navigate the complexities of energy production and safety.
Call to Action
If you found this article insightful, consider sharing it with others or exploring additional resources on nuclear safety and ethical energy production. Together, we can foster a safer and more informed society.
Article Recommendations
- Foster Sarell Expert Advice Insights
- Tanner Mckee Stanford Football Stars Journey
- Legendary Ricky Horton Baseball Highlights